The restoration works that started on the Acropolis in 2017 and were funded by the OP Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship, and Innovation 2014-2020 (EPANEK), will have been completed within the agreed time schedule by June 2023, despite the problems caused by covid-19. Some of the works have already been concluded.
Consolidation interventions focused on the Parthenon and the Walls, and conservation works in most of the monuments on the archaeological site.
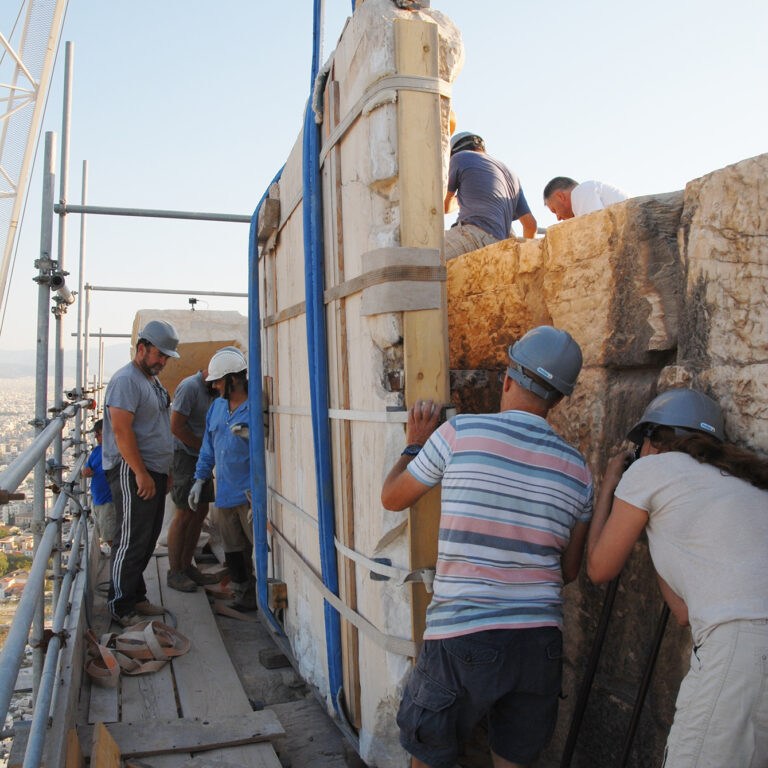
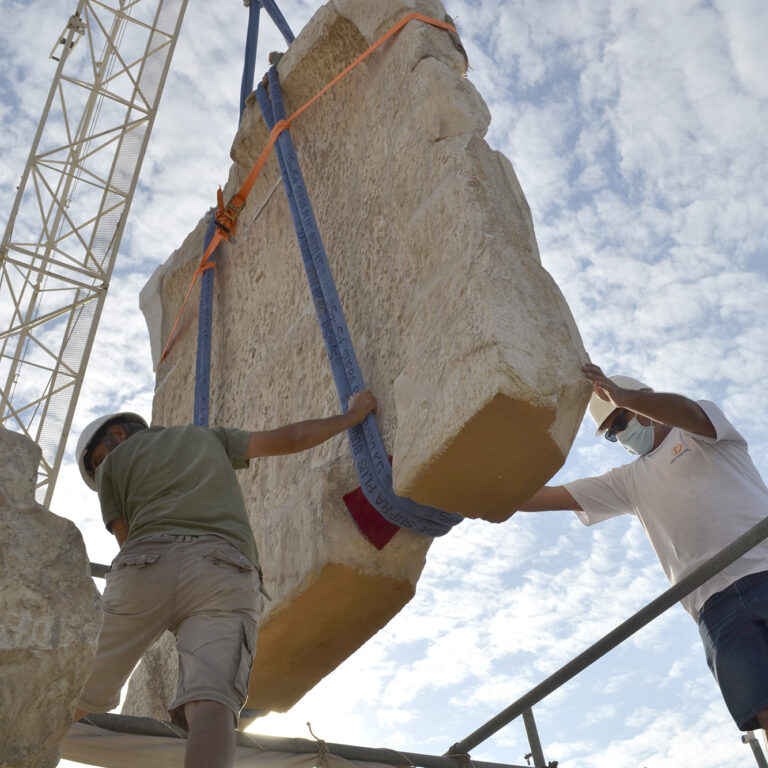
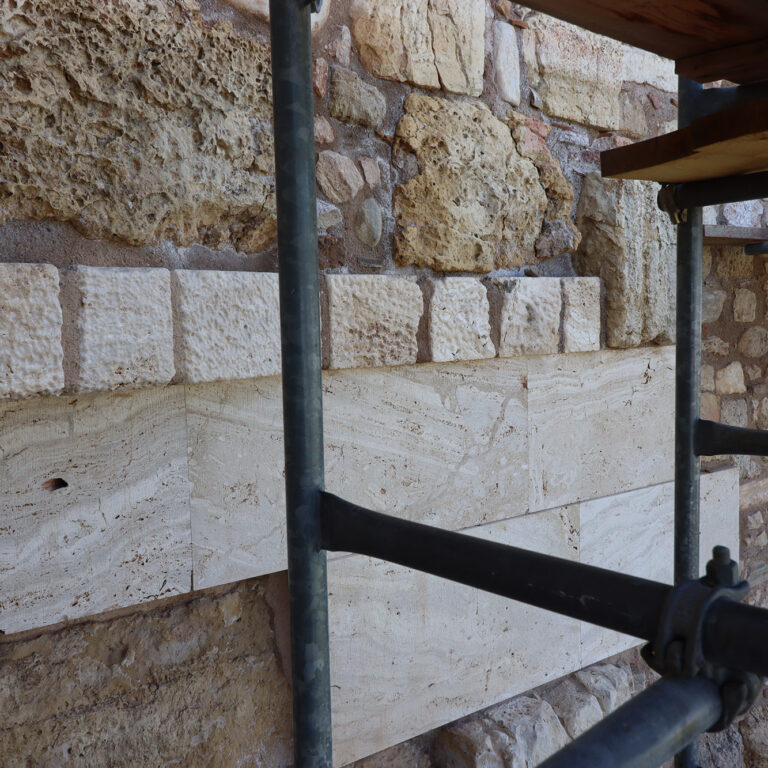
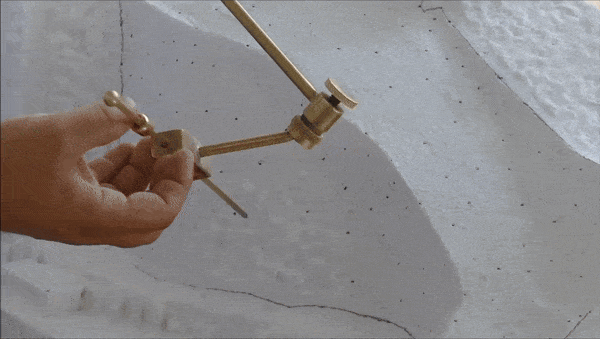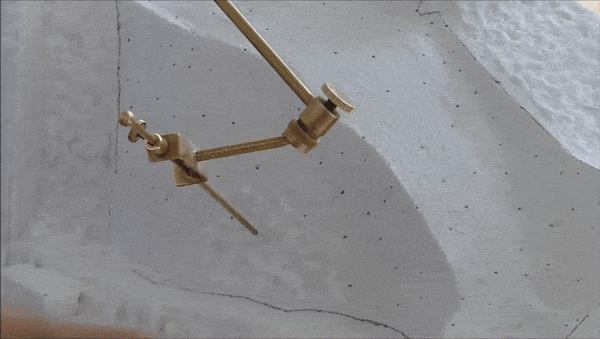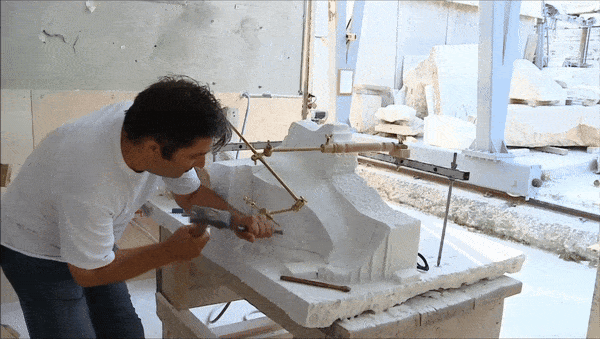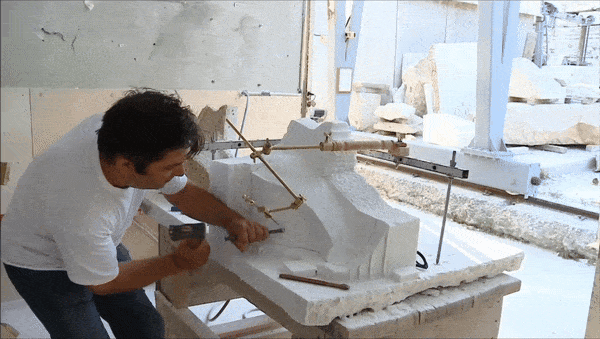
The consolidation interventions included dismantling of the areas where structural problems had been identified, removal of inappropriate materials (concrete and iron) that had been used during pre-war interventions, structural restoration of fragmented architectural members in laboratories, fillings with the use of new marble in areas where there was an imperative need, repositioning of the restored ancient and new architectural members and restoring the monuments structure conforming to their authentic construction system.
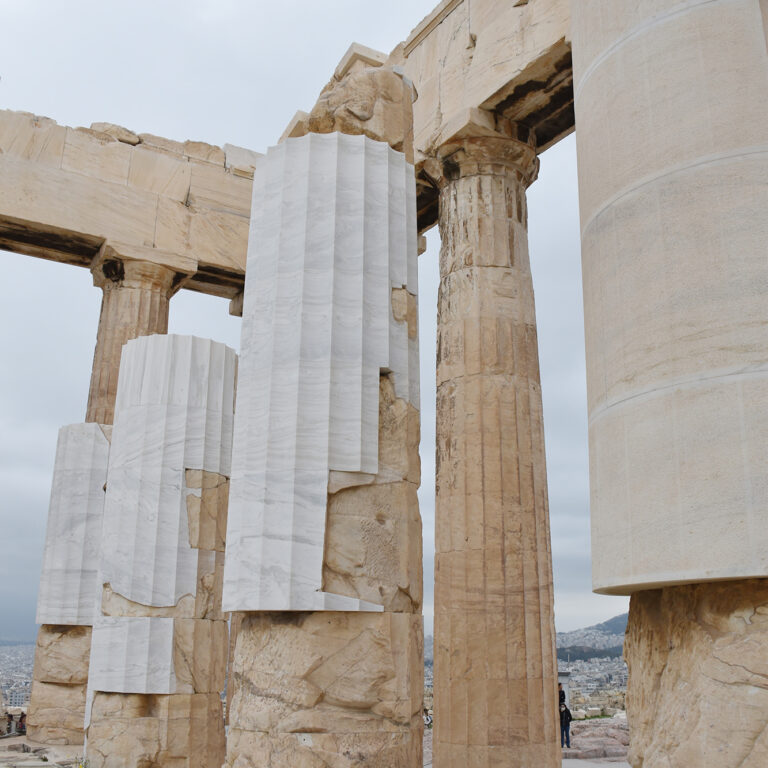
What was completed on the Parthenon was the restoration of the orthostate and the 1st row of the North wall of the cella, while the restoration of the 2nd row is still in progress. The flutes in the fillings of the Pronaos 3rd column and the new column drums were aptly carved. On the west side of the monument the restoration of the horizontal geison, the orthostates of the tympanum and the blocks of the backing wall were restored. The works regarding the repositioning of the dismantled architectural members of the tympanum and the backing wall are continuing. For the needs of the works 60 m³ of marble were bought and cut in suitable dimensions. (Sub-work 2).
In the circuit walls the area B17 (027.500m – 035.000m) of the north wall was restored, the retaining wall of the Mycenaean stairway was secured and exposed, whereas a system of instrumental observation (a network of accelerometers and optical fibres) was used for collecting additional measurements.
Conservation works were completed on the Parthenon West pediment, on the North wall of the cella, on a column of the Pronaos and on columns of the Opisthonaos. Moreover, on the North Wall, in the area of the NW building (North exterior facade), and in the area B14 (interior). The completed works at the Propylaea involved the conservation of the colonnade and the entablature of the North Wing; works on its portal wall are in progress. Conservation works on the pedestal of the Agrippa monument also continue.
The completed works regarding the management of scattered architectural members involved the cataloguing of selected architectural members in order to store or exhibit them in the Old Acropolis Museum, the documentation and management of 400 scattered architectural members from the area of the Chalkotheke, the identification and documentation of 50 architectural members from the temple of Athena Polias and the structural restoration of 25 large architectural members.
Laboratory analyses were conducted to identify the authentic materials and the degradation products, and to also look for materials that are suitable for the conservation interventions in marble and limestone areas.
All the undertaken works are systematically documented. Ongoing works include the addition of the intervention documents to a database, the filming of the works, the digitalisation of conventional archive material, the designing and uploading of the application “An Ancient Temple”, the publication of educational printed material on the subject of ancient Greek architecture and booklets for students and teachers.
A three-dimensional digital model of the Propylaea North wing was made, while photogrammetric surveying is still being conducted in the areas of the Parthenon where interventions are being carried out (Sub-work 8). New information signs were place on various places of the archaeological site.
The benefits of the work. The main intents of the programme were to protect the Acropolis monuments, since 1987 inscribed in the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites, not only against the effects of climate change, but also from failed previous conservation interventions that had used inappropriate materials. Restoring the problems of the monuments, designing, and providing the public with many applications containing information and educational materials relevant with the exercised interventions, contribute to a better understanding of the values the monuments of classical antiquity, as symbols of western civilization, represent.
The restoration of the Acropolis monuments follows a specific methodology, which has been developed for this specific case and has already become a model for the restoration of other monuments of classical architecture in Greece and other Mediterranean countries.
The main features of the work are:
- The steady and constant relation of the works with research. Many research programmes are undertaken by the scientific personnel of the Service, either by the Service itself or in collaboration with educational Institutions or other research bodies of our country; the goal of these programmes is to solve theoretical and technical problems that surface during the interventions.
- The systematic implementation of modern technological innovations.
- Scheduling the works and conducting the relevant studies, organised by YSMA’s specialised scientific personnel; as well as the implementation of the works by experienced contractors under the supervision of YSMA’s staff ensuring as such their timely and most efficient delivery.
- Establishing, within the context of the works, a highly specialised and experienced personnel competent to carry out any work concerning the restoration interventions in classical monuments; a factor that can also influence the undertaking of similar interventions in all the monuments of our country.
- The development of suitable practical knowledge and ability to speed up the works.
In addition, the worksites are supplied with highly specialised and innovative equipment combining modern technology with ancient traditional tools used for construction and stone carving.
The implementation of restoration and conservation interventions, by using material and methods compatible with the unique nature of the monument, is of high priority in order to ensure the conservation and protection of the natural and cultural heritage. The methodology employed in the interventions in the Acropolis monuments, whose main characteristics are the preservation of the structural system of the monuments and the use of materials compatible with the original ones, does not only confirm their protection and their preservation, but also reduces the carbon footprint when compared with actions taken in the past, satisfying as such a modern understanding regarding the adoption of actions that promote the green transition and assure measures to prevent and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
The good practice, based on the principles and methodology implemented on the restoration of the Acropolis monuments, has been awarded three times by EUROPA NOSTRA.
Most of the events that promote the work can be accessed on the Internet, on the website of the Acropolis Restoration Service: https://www.ysma.gr/
Material relevant to the work on the Acropolis can be accessed in the following links:
Films:
Restoration works on the Acropolis monuments 2017-2021 (with English subtitles)
Interventions in the Acropolis. The Documentation archive (with English subtitles)
Educational application & educational printed material:
An ancient temple (Greek & English)
A map for children to explore the Acropolis (Greek & English)
Online promotion event: